Balance of payments. The UK balance of payments current account for Q1 (2020) is sitting £-2.1 billion This article will explain what the balance of payments is and will explain its components including the current account and the balance of trade in goods and services.
Welcome to Simply Economics. This article is the fourth in a series to explain economics to those who want to broaden their scope of the subject. Click here to find out more about the series.
WHAT IS THE BALANCE OF PAYMENTS?
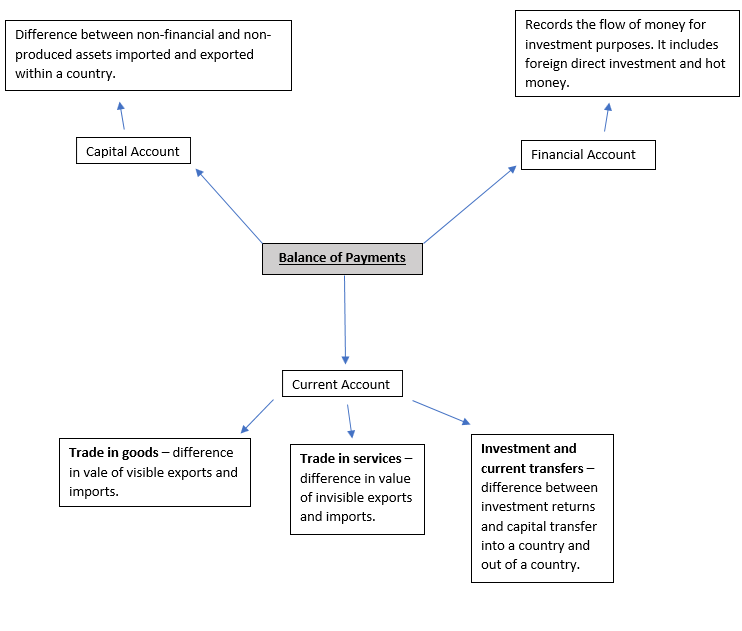
The balance of payments is the difference in value between the financial transactions in and out of a country. It I composed of 3 main accounts:
CURRENT ACCOUNT
The current account is split into a few components:
- Trade in Goods – Trade in goods is also known as visible trade. The trade in goods measures the movement of raw materials (oil, minerals etc), semi-manufactured goods (car parts, phone parts etc) and finished goods (cars, phones, tablets etc).
Visible Exports are goods that are sold to foreign countries and they bring money into the country which would have a positive impact on the current account.
Visible Imports are goods that are bought into the country and they take money out of the country. This has a negative impact on the balance of payments.
The trade in goods is the visible exports minus the visible imports.
- Trade in Services – Trade in services is also known as invisible trade. It measures many services ranging from banking to travel and tourism.
Invisible exports are bought by foreigners and bring money into the country; therefore, it would have a positive impact on the balance of payments.
Invisible imports are bought by domestic consumers and take money out of the country; therefore, to would have a negative impact on the balance of payments.
- Investment (primary income) and current transfers (secondary income) – Investment income the total income from interest, profit and dividends due to capital investments abroad.
For example, if British person buys a share of a French company, then the dividends appear on the current account, not the shares.
Current transfers are the movement of funds where there are no goods or services traded. An example of this would be countries paying taxes for being part of a trading bloc (EU). Another example of this is when people send money to relatives who live abroad.
CURRENT ACOUNT BALANCE, DEFICIT AND SURPLUS
- Current account balance – The difference between the total value of imports and the total value of exports is the current account balance.
- Current account surplus – When the total value of exports is greater than the total value of imports then the current account is said to be in a surplus. Countries with high export to import value ratios are China and Germany.
- Current account deficit – When the total value of imports is greater than the total value of exports the current account is said to be in a deficit. Countries with high import to export value ratios are Greece and Portugal.
FINANCIAL ACCOUNT
The second component of the balance of payments is the financial account. This records the flow of money for investment purposes which includes:
- Foreign Direct Investments – This is an investment into a business or asset by a person or firm in a foreign country. It can be buying a business or expanding operations into a foreign country (like TNCs).
- Hot Money – Hot money is the capital that is transferred from one country to another in order to capitalise from changes in interest and exchange rates. For example, if the base rate of interest is 0% is the USA but is 5% in Brazil then the owner of the capital would benefit more if they held cash in a Brazilian bank account rather than an American one.
CAPITAL ACCOUNT
This account measures the net change in the non-financial and non-produced assets. Examples of such assets are patents, copywrites and trademarks.
BALANCE OF PAYMENTS IMBALANCES AND WHAT THEY MEAN
A balance of payments deficit is not always a bad thing. This is because it can be a sign that living standards are rising because consumers can afford to import more goods. However, it starts to be a problem when a country cannot afford to hold reserves of foreign currencies.
This is because when a country has a balance of payments deficit and it doesn’t have enough reserves of foreign currency then it can lead to a depreciation of the country’s currency. This would cause imports to increase in price. This can cause unemployment in the domestic economy as import costs are rising faster other trading partners which reduces international competitiveness.
However, there is another side to the coin. If a currency depreciates it causes the cost of exports to decrease. This means domestic products become more affordable for foreign countries which will encourage those countries to buy domestic exports. This would have a positive effect on the balance of payments and could possibly cause a surplus.
Feel free to ask any questions and sign up below for the latest updates. Click here for more articles. For more articles in the General Articles series, click here.
What is Quantitative Easing (QE)
This article will explain the key concepts of Quantitative Easing. It will explain how Quantitative…
11. Taxes
This article will go through the different types of taxes and will explain where the…
10. Consumer and Producer Surplus
This article will explain consumer and producer surplus are and will also discuss the impact…
What are shares and why buy them?
What are shares and why buy them? This article will explain why people buy shares…
4. Balance of Payments
Balance of payments. The UK balance of payments current account for Q1 (2020) is sitting…
3. Employment and Unemployment
Employment and unemployment. This article will explain what unemployment is and how it is measured….
2. Inflation
Inflation. This article will explain the basic principles of CPI inflation and will define basic…
1. What is GDP and how is it measured?
What is GDP and how is it measured? GDP dropped over 20% in April in…
9. Price Determination
Price determination. This article will explain what an equilibrium price is and how an equilibrium…
3 . Virgin Galactic – The next Tesla?
Virgin Galactic – the next Tesla? This article will discuss the future of Virgin Galactic…
8.2 Determinants of Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
Determinants of price elasticity of supply. This article will explain what determines the price elasticity…
8. Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
Price elasticity of supply. This article will explain what price elasticity of supply is and…
7.2 Total Revenue and Price Elasticity of Demand.
Total revenue and price elasticity of demand. This article will explain what determines the price…
7.1 PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND (PED)
Price elasticity of demand. This article will explain what PED is and will go through…
6. SUPPLY THEORY
Supply theory. This article will explain what the supply theory is and how the supply…
5. Demand Theory
Demand theory. This article explains what the demand theory is and will go on to…
WHY IS THE US STOCK MARKET RALLYING?
Why is the US stock market rallying? This article explains why the Us stock market…
2. Gold uncovered
Gold uncovered. Is gold a good investment during a recession? This article explains why gold…
4. Types of Economies
Types of economies. How many different types of economies are the and how are resources…
3. Division and Specialisation of Labour.
Division and specialisation of labour. How does it affect the efficiency of production? This article…
2. Production Possibility Frontiers (PPF).
What are production possibility frontiers? This article explains what PPFs are and what causes movements…
What next for the US stock market?
We have just entered one of the fastest market corrections in history. What happened and…
1. The Definition of Economics
What is economics? This article explains the definition of economics and the fundamental assumptions held…
Why the Stock Market is Going to Crash.
Why is the stock market going to crash? Since the crash in March, markets across…

























How to find out the total import value?
You can find information on each country on this website
https://wits.worldbank.org/countrystats.aspx?lang=en
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.