This article will explain consumer and producer surplus are and will also discuss the impact of increases in consumer and producer surplus. Furthermore, the article will investigate how the price elasticity of demand can affect the incidence of such surpluses.
Welcome to Simply Economics. This article is the twelfth in a series to explain economics to those who want to broaden their scope of the subject. Click here to find out more about the series. This article explains the determinants of price elasticity of supply.
WHAT IS CONSUMER SURPLUS
Consumer surplus is the extra amount of money that consumers are willing to pay for a good above the equilibrium price, it is the satisfaction gained from a product after accounting for its price.
WHAT IS PRODUCER SURPLUS
Producer surplus is the extra amount of money producers are paid to supply a product above what they are willing to supply the product for.
Below is a graph which shows the area of producer and consumer surplus.
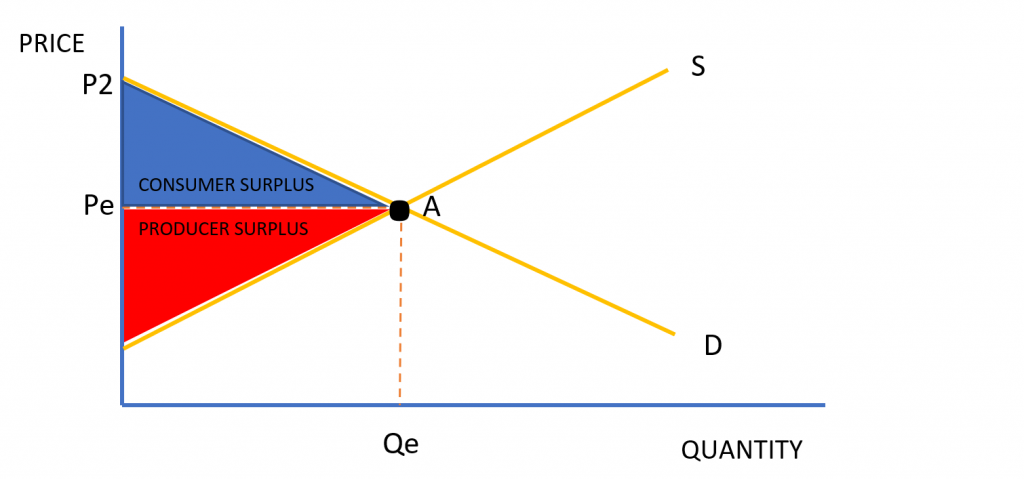
In Figure 1, the areas of consumer and producer surplus are shown on a simple supply and demand diagram.
Pe is the equilibrium price and Qe is the equilibrium quantity of the supply and demand of the good (i.e. when supply is equal to demand).
From Figure 1 the following formula can be derived for consumer and producer surplus:
CONSUMER SURPLUS = ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() (Qe x (P2 – Pe)) ÷ 2.
(Qe x (P2 – Pe)) ÷ 2.![]()
PRODUCER SURPLUS = ![]() (Qe x (Pe – P1)) ÷ 2.
(Qe x (Pe – P1)) ÷ 2.
WHERE:
- Qe is the equilibrium price.
- Pe is the equilibrium price.
- P2 is the y-intercept of the demand curve.
- P1 is the y-intercept of the supply curve.
WHERE DO THE EQUATIONS COME FROM?
As shown by Figure 1, the areas of consumer and producer surplus are right-angled triangles. The area of a right-angled triangle is (base x height) ÷ 2.
Therefore, for consumer surplus if the base is Qe and the height to be the difference between P2 and Pe then the formula to find consumer surplus would be:
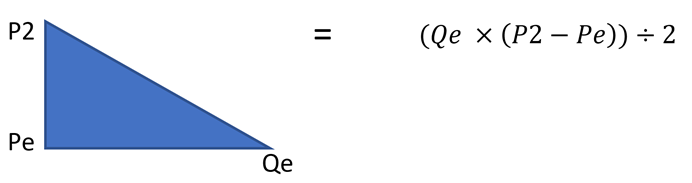
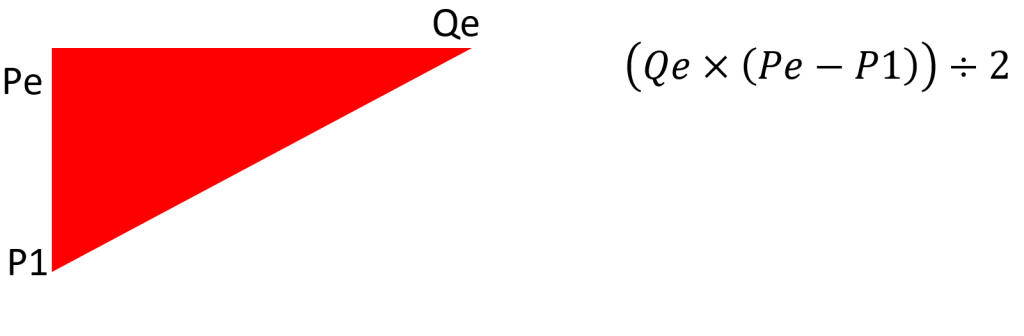
Similarly, for producer surplus if the base is taken to be Qe and the height to be the difference between Pe and P1 then to formula to find producer surplus would be:
EFFECTS OF A CHANGE IN DEMAND AND SUPPLY
An outward shift in the demand curve will cause and increase in both consumer and producer surplus. However, this assumes all other factors including the supply of the good remains the same.
Similarly, if there is an outward shift in the supply curve of a good then it will cause an increase in the consumer and producer surplus.
On the other hand, if there is an inward shift in the demand or supply curves then it will cause the consumer and producer surpluses to be reduced. In order to develop your understanding, it is good practise to draw out these changes.
THE INCIDENCE OF CONSUMER AND PRODUCER SURPLUS
In theory, if the price elasticity of demand is equal to -1 and the price elasticity of supply is equal to 1, the consumer surplus and producer surplus would be the same. However, it is likely that the price elasticity of demand and price elasticity of supply will not equal -1 and 1, respectively.
This is important to understand because a change in the PED and PES influences the size of the producer and consumer surplus as shown below in Figure 3.
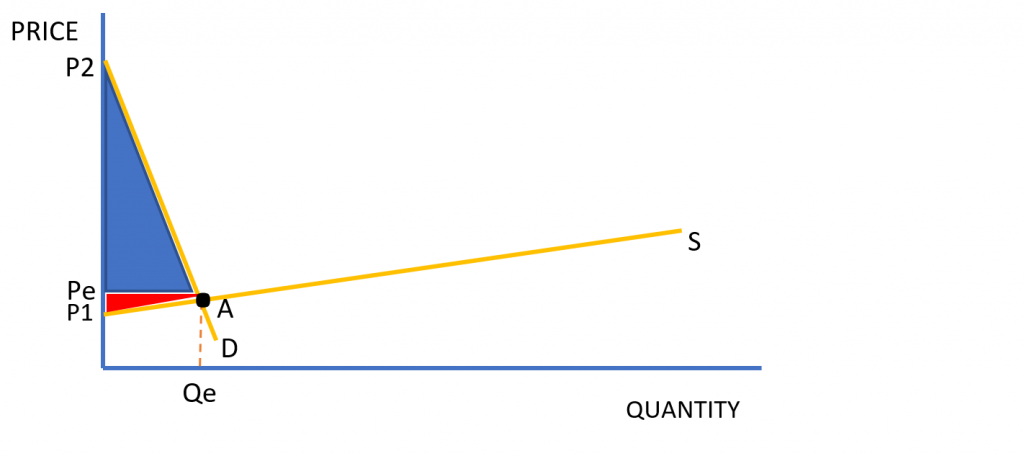
As shown by Figure 3, if a good or service has inelastic demand and elastic supply then most of the surplus will fall on the consumer. This is beneficial for the consumer because although they are willing to pay a lot more for the good (P2), they pay much less for the good (Pe), therefore the welfare gain for the consumer high.
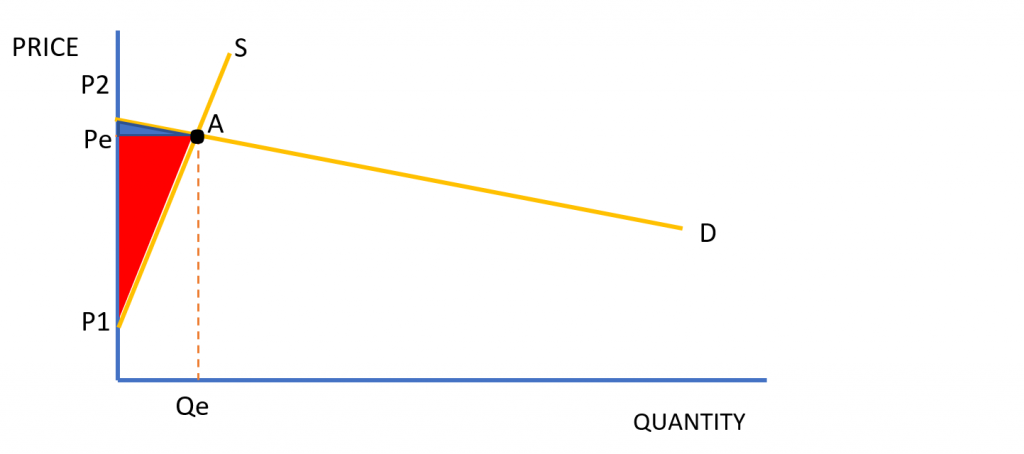
As shown by Figure 4, if a good or service has elastic demand and inelastic supply then most of the surplus will fall on the producer. This is beneficial for the producer because although they are willing to supply good for a lot less (P1), they sell it for much more (Pe), therefore the welfare gain for the producer is high.
Overall, consumer and producer surplus shows the welfare gained by the consumer and producers. However, the amount of welfare gained from selling/purchasing a good can vary due to the PED and PES of the good.
Feel free to ask any questions and sign up below for the latest updates. Click here for more articles. For more articles in the Economics for Beginners series, click here.
What is Quantitative Easing (QE)
This article will explain the key concepts of Quantitative Easing. It will explain how Quantitative…
11. Taxes
This article will go through the different types of taxes and will explain where the…
10. Consumer and Producer Surplus
This article will explain consumer and producer surplus are and will also discuss the impact…
What are shares and why buy them?
What are shares and why buy them? This article will explain why people buy shares…
4. Balance of Payments
Balance of payments. The UK balance of payments current account for Q1 (2020) is sitting…
3. Employment and Unemployment
Employment and unemployment. This article will explain what unemployment is and how it is measured….
2. Inflation
Inflation. This article will explain the basic principles of CPI inflation and will define basic…
1. What is GDP and how is it measured?
What is GDP and how is it measured? GDP dropped over 20% in April in…
9. Price Determination
Price determination. This article will explain what an equilibrium price is and how an equilibrium…
3 . Virgin Galactic – The next Tesla?
Virgin Galactic – the next Tesla? This article will discuss the future of Virgin Galactic…
8.2 Determinants of Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
Determinants of price elasticity of supply. This article will explain what determines the price elasticity…
8. Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
Price elasticity of supply. This article will explain what price elasticity of supply is and…
7.2 Total Revenue and Price Elasticity of Demand.
Total revenue and price elasticity of demand. This article will explain what determines the price…
7.1 PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND (PED)
Price elasticity of demand. This article will explain what PED is and will go through…
6. SUPPLY THEORY
Supply theory. This article will explain what the supply theory is and how the supply…
5. Demand Theory
Demand theory. This article explains what the demand theory is and will go on to…
WHY IS THE US STOCK MARKET RALLYING?
Why is the US stock market rallying? This article explains why the Us stock market…


















what is the advantage if there is a surplus?
A trade surplus (where a country exports more goods and services than it imports) can provide several benefits to an economy: Increased Foreign Currency Reserves: A trade surplus means that a country is earning more in foreign currencies than it is spending, which can increase its foreign currency reserves. Increased Economic Growth: Exporting goods and services can stimulate economic growth by creating jobs and generating income for businesses. Improved Balance of Payments: A trade surplus helps improve a country’s balance of payments, which is a record of all its financial transactions with the rest of the world. Increased Investment: A… Read more »
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!